📸 Vision model scan¶
The giskard-vision library is under development. For now, only landmark detection models are available.
The Giskard python library provides an automatic scan functionality designed to automatically detect potential vulnerabilities affecting your ML model. It enables you to proactively identify and address key issues to ensure the reliability, fairness, and robustness of your Machine Learning models.
Before starting¶
Before starting, make sure you have installed both the base and vision libraries of Giskard:
pip install giskard giskard-vision
Step 1: Wrap your dataset¶
To scan your model, start by wrapping your dataset with DataLoaderBase. Your class should override:
load_image_from_filethat loads an image as anp.ndarrayload_marks_from_filethat returns landmark coordinates from a file.
⚠️ Warning
It’s highly recommended that you wrap your data before preprocessing so that you can easily interpret the scan results.
from giskard_vision.landmark_detection.dataloaders.base
class DataLoaderLandmarkDetection(DataLoaderBase):
@classmethod
def load_image_from_file(cls, image_file: Path) -> np.ndarray:
# use image_file to read the image into a numpy array
return cv2.imread(str(image_file))
@classmethod
def load_marks_from_file(cls, mark_file: Path):
# use mark_file path to populate the numpy array
return np.array(..., dtype=float)
giskard_dataset = DataLoaderLandmarkDetection(images_dir_path=..., landmarks_dir_path=...)
Step 2: Wrap your model¶
Next, wrap your model with FaceLandmarksModelBase. It should contain a method predict_image that returns landmarks as np.ndarray, as shown here:
from giskard_vision.landmark_detection.models.base import FaceLandmarksModelBase
class ModelLandmarkDetection(FaceLandmarksModelBase):
def __init__(self, model):
super().__init__(n_landmarks=68, n_dimensions=2, name="MyModel")
self.model = model
def predict_image(self, image: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
return self.model.predict_image(image)
mymodel = ...
giskard_model = ModelLandmarkDetection(model = mymodel)
Step 3: Scan your model¶
You can now scan your model. For this guide, we’ll use a demo dataloader and an OpenCV model. After completing steps 1 and 2, you can replace them with your own dataloader and model wrapper.
from giskard_vision.landmark_detection.models.wrappers import OpenCVWrapper
from giskard_vision.landmark_detection.demo import get_300W
giskard_model = OpenCVWrapper()
giskard_dataset = get_300W()
scan_results = giskard_vision.scan(giskard_model, giskard_dataset)
display(scan_results) # in your notebook
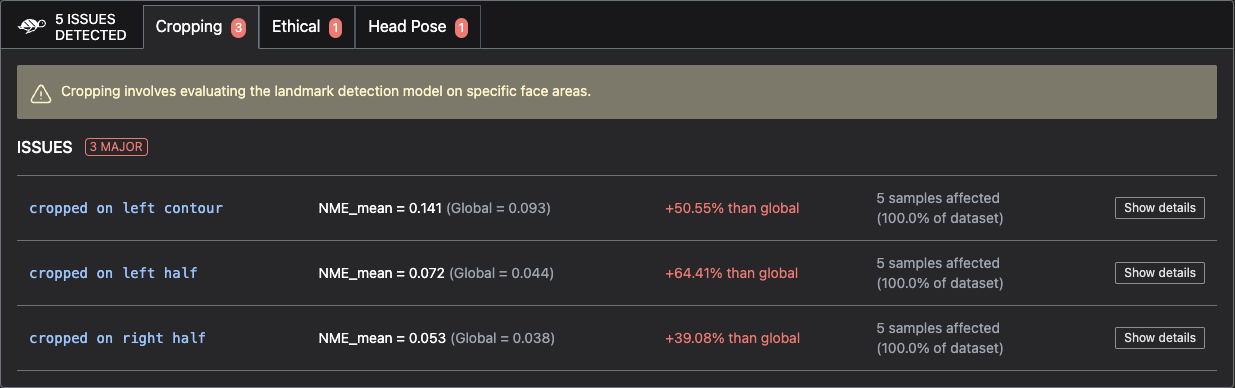
If you are not working in a notebook or want to save the results for later, you can save them to an HTML file like this:
scan_results.to_html("model_scan_results.html")

