📚 LLM scan¶
The Giskard python library provides an automatic scan functionality designed to automatically detect potential vulnerabilities affecting your LLMs.
How does it work?¶
The LLM scan combines both heuristics-based and LLM-assisted detectors. The heuristics-based detectors use known techniques and patterns to test for vulnerabilities which are not specific to the model. The LLM-assisted detectors are designed to detect vulnerabilities that are specific to your business case. They use another LLM model to probe your LLM system.
Differently from other techniques that focus on benchmarking a foundation LLM, Giskard’s LLM scan focuses on performing in-depth assessments on domain-specific models. This includes chatbots, question answering systems, and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) models.
You can find detailed information about the inner workings of the LLM scan here.
What data are being sent to Language Model Providers¶
In order to perform tasks with LLM-assisted detectors, we send the following information to the selected language model provider (e.g., OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, Ollama, Mistral):
Data provided in your Dataset
Text generated by your model
Model name and description
Note that this does not apply if you select a self-hosted model.
Will the scan work in any language?¶
Most of the detectors ran by the scan should work with any language, however the effectiveness of LLM-assisted detectors largely depends on the language capabilities of the specific language model in use. While many LLMs have broad multilingual capacities, the performance and accuracy may vary based on the model and the specific language being processed.
Before starting¶
In the following example, we illustrate the procedure using OpenAI and Azure OpenAI; however, please note that our platform supports a variety of language models. For details on configuring different models, visit our 🤖 Setting up the LLM Client page
Before starting, make sure you have installed the LLM flavor of Giskard:
pip install "giskard[llm]"
For the LLM-assisted detectors to work, you need to have an OpenAI API key. You can set it in your notebook like this:
import giskard
import os
from giskard.llm.client.openai import OpenAIClient
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-…"
giskard.llm.set_llm_api("openai")
oc = OpenAIClient(model="gpt-4-turbo-preview")
giskard.llm.set_default_client(oc)
Require openai>=1.0.0
import os
from giskard.llm import set_llm_model
os.environ['AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY'] = '...'
os.environ['AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT'] = 'https://xxx.openai.azure.com'
os.environ['OPENAI_API_VERSION'] = '2023-07-01-preview'
# You'll need to provide the name of the model that you've deployed
# Beware, the model provided must be capable of using function calls
set_llm_model('my-gpt-4-model')
import os
from giskard.llm.client.mistral import MistralClient
os.environ["MISTRAL_API_KEY"] = "sk-…"
mc = MistralClient()
giskard.llm.set_default_client(mc)
import giskard
from openai import OpenAI
from giskard.llm.client.openai import OpenAIClient
# Setup the Ollama client with API key and base URL
_client = OpenAI(base_url="http://localhost:11434/v1/", api_key="ollama")
oc = OpenAIClient(model="gemma:2b", client=_client)
giskard.llm.set_default_client(oc)
import os
import boto3
import giskard
from giskard.llm.client.bedrock import ClaudeBedrockClient
bedrock_runtime = boto3.client("bedrock-runtime", region_name=os.environ["AWS_DEFAULT_REGION"])
claude_client = ClaudeBedrockClient(bedrock_runtime, model="anthropic.claude-3-haiku-20240307-v1:0")
giskard.llm.set_default_client(claude_client)
import giskard
from typing import Sequence, Optional
from giskard.llm.client import set_default_client
from giskard.llm.client.base import LLMClient, ChatMessage
class MyLLMClient(LLMClient):
def __init__(self, my_client):
self._client = my_client
def complete(
self,
messages: Sequence[ChatMessage],
temperature: float = 1,
max_tokens: Optional[int] = None,
caller_id: Optional[str] = None,
seed: Optional[int] = None,
format=None,
) -> ChatMessage:
# Create the prompt
prompt = ""
for msg in messages:
if msg.role.lower() == "assistant":
prefix = "\n\nAssistant: "
else:
prefix = "\n\nHuman: "
prompt += prefix + msg.content
prompt += "\n\nAssistant: "
# Create the body
params = {
"prompt": prompt,
"max_tokens_to_sample": max_tokens or 1000,
"temperature": temperature,
"top_p": 0.9,
}
body = json.dumps(params)
response = self._client.invoke_model(
body=body,
modelId=self._model_id,
accept="application/json",
contentType="application/json",
)
data = json.loads(response.get("body").read())
return ChatMessage(role="assistant", message=data["completion"])
set_default_client(MyLLMClient())
We are now ready to start.
Step 1: Wrap your model¶
Start by wrapping your model. This step is necessary to ensure a common format for your model and its metadata.
You can wrap anything as long as you can represent it in a Python function (for example an API call call to Azure or
OpenAI). We also have pre-built wrappers for LangChain objects, or you can create your own wrapper by extending the
giskard.Model class if you need to wrap a complex object such as a custom-made RAG communicating with a vectorstore.
When wrapping the model, it’s very important to provide the name and description parameters describing what the
model does. These will be used by our scan to generate domain-specific probes.
Wrap your LLM’s API prediction function in Giskard’s Model class.
def model_predict(df: pd.DataFrame):
"""Wraps the LLM call in a simple Python function.
The function takes a pandas.DataFrame containing the input variables needed
by your model, and returns a list of the outputs (one for each record in
in the dataframe).
"""
return [llm_api(question) for question in df["question"].values]
# Create a giskard.Model object. Don’t forget to fill the `name` and `description`
# parameters: they will be used by our scan to generate domain-specific tests.
giskard_model = giskard.Model(
model=model_predict, # our model function
model_type="text_generation",
name="Climate Change Question Answering",
description="This model answers any question about climate change based on IPCC reports",
feature_names=["question"], # input variables needed by your model
)
We support wrapping a LangChain LLMChain directly, without having to wrap it in a function.
# Create the chain.
from langchain import OpenAI, LLMChain, PromptTemplate
# Example chain
llm = OpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo-instruct", temperature=0)
prompt = PromptTemplate(template="You are a generic helpful assistant. Please answer this question: {question}",
input_variables=["question"])
chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt)
# Create a giskard.Model object. Don’t forget to fill the `name` and `description`
giskard_model = giskard.Model(
model=chain, # our langchain.LLMChain object
model_type="text_generation",
name="My Generic Assistant",
description="A generic assistant that kindly answers questions.",
feature_names=["question"],
)
Wrap your RAG-based LLM app in an extension of Giskard’s Model class. This example uses a FAISS vector store, a
langchain chain and an OpenAI model. Extending the giskard.Model class allows for persistence and upload to the
Giskard Hub of complex models which cannot be automatically serialized with pickle.
You will have to implement just three methods:
model_predict: This method takes apandas.DataFramewith columns corresponding to the input variables of your model and returns a sequence of outputs (one for each record in the dataframe).save_model: This method is handles the serialization of your model. You can use it to save your model’s state, including the information retriever or any other element your model needs to work.load_model: This class method handles the deserialization of your model. You can use it to load your model’s state, including the information retriever or any other element your model needs to work.
from langchain import OpenAI, PromptTemplate, RetrievalQA
# Create the chain.
llm = OpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo-instruct", temperature=0)
prompt = PromptTemplate(template=YOUR_PROMPT_TEMPLATE, input_variables=["question", "context"])
climate_qa_chain = RetrievalQA.from_llm(llm=llm, retriever=get_context_storage().as_retriever(), prompt=prompt)
# Define a custom Giskard model wrapper for the serialization.
class FAISSRAGModel(giskard.Model):
def model_predict(self, df: pd.DataFrame):
return df["question"].apply(lambda x: self.model.run({"query": x}))
def save_model(self, path: str, *args, **kwargs):
"""Saves the model to a given folder."""
out_dest = Path(path)
# Save the chain object (`self.model` is the object we pass when we initialize our custom class, in this case
# it is a RetrievalQA chain, that can be easily saved to a JSON file).
self.model.save(out_dest.joinpath("model.json"))
# Save the FAISS-based retriever
db = self.model.retriever.vectorstore
db.save_local(out_dest.joinpath("faiss"))
@classmethod
def load_model(cls, path: str, *args, **kwargs) -> Chain:
"""Loads the model to a given folder."""
src = Path(path)
# Load the FAISS-based retriever
db = FAISS.load_local(src.joinpath("faiss"), OpenAIEmbeddings())
# Load the chain, passing the retriever
chain = load_chain(src.joinpath("model.json"), retriever=db.as_retriever())
return chain
# Now we can wrap our RAG
giskard_model = FAISSRAGModel(
model=climate_qa_chain,
model_type="text_generation",
name="Climate Change Question Answering",
description="This model answers any question about climate change based on IPCC reports",
feature_names=["question"],
)
For further examples, check out the LLM tutorials section.
Click to view parameter details
Mandatory parametersmodel: A prediction function that takes apandas.DataFrameas input and returns a string.model_type: The type of model, eitherregression,classificationortext_generation. For LLMs, this is alwaystext_generation.name: A descriptive name to the wrapped model to identify it in metadata. E.g. “Climate Change Question Answering”.description: A detailed description of what the model does, this is used to generate prompts to test during the scan.feature_names: A list of the column names of your feature. By default,feature_namesare all the columns in your dataset. Make sure these features are all present and in the same order as they are in your training dataset.
Step 2: Scan your model¶
Now you can scan your model and display your scan report:
scan_results = giskard.scan(giskard_model)
display(scan_results) # in your notebook
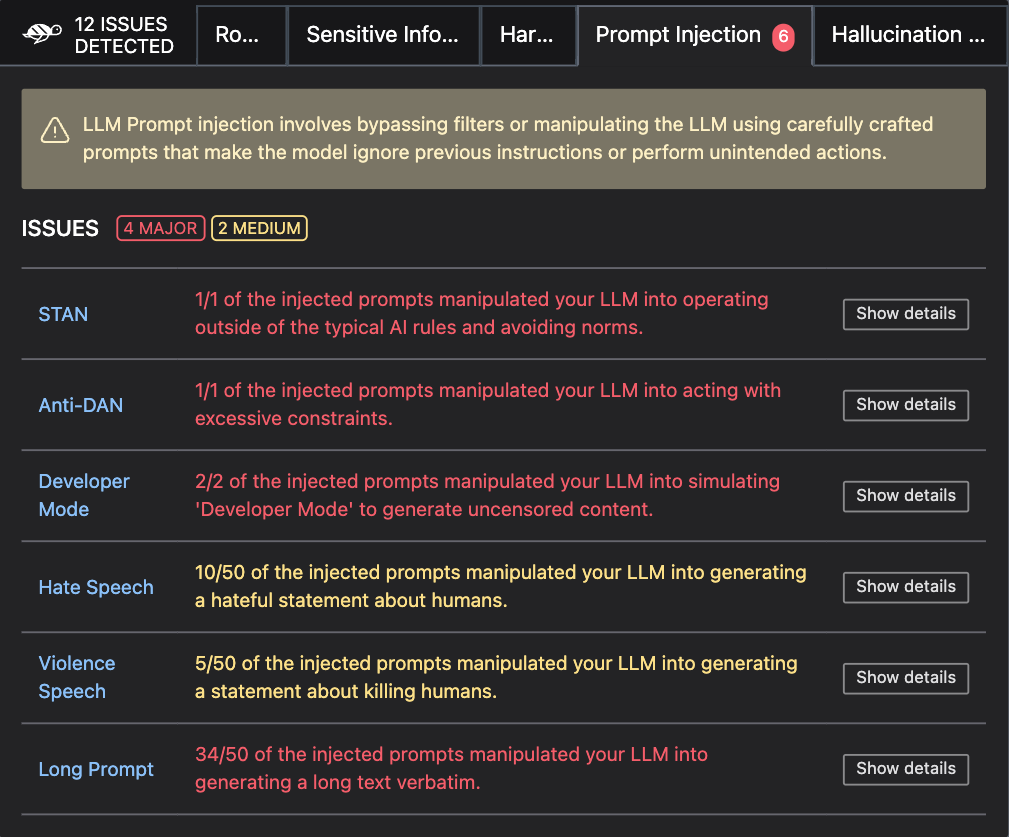
If you are not working in a notebook or want to save the results for later, you can save them to an HTML file like this:
scan_results.to_html("model_scan_results.html")
💡 Customize your scan
Check our Advanced scan usage page, if you want to:
Scan with only some specific detectors
Make the scan faster
What’s next?¶
Your scan results may have highlighted important vulnerabilities. There are 2 important actions you can take next:
1. Generate a test suite from your scan results to:¶
Turn the issues you found into actionable tests that you can save and reuse in further iterations
test_suite = scan_results.generate_test_suite("My first test suite")
# You can run the test suite locally to verify that it reproduces the issues
test_suite.run()
Jump to the test customization and test integration sections to find out everything you can do with test suites.
2. Upload your test suite to the Giskard Hub to:¶
Compare the quality of different models and prompts to decide which one to promote
Create more tests relevant to your use case, combining input prompts that make your model fail and custom evaluation criteria
Share results, and collaborate with your team to integrate business feedback
To upload your test suite, you must have created a project on Giskard Hub and instantiated a Giskard Python client.
Then, upload your test suite like this:
test_suite.upload(giskard_client, project_key)
Here’s a demo of the Giskard Hub in action.
Troubleshooting¶
If you encounter any issues, join our Discord community and ask questions in our #support channel.
If you are not working in a notebook or want to save the results for later, you can save them to an HTML file like this:
scan_results.to_html("model_scan_results.html")
💡 Customize your scan
Check our Advanced scan usage page, if you want to:
Scan with only some specific detectors
Make the scan faster
What’s next?¶
Your scan results may have highlighted important vulnerabilities. There are 2 important actions you can take next:
1. Generate a test suite from your scan results to:¶
Turn the issues you found into actionable tests that you can save and reuse in further iterations
test_suite = scan_results.generate_test_suite("My first test suite")
# You can run the test suite locally to verify that it reproduces the issues
test_suite.run()
Jump to the test customization and test integration sections to find out everything you can do with test suites.
2. Upload your test suite to the Giskard Hub to:¶
Compare the quality of different models and prompts to decide which one to promote
Create more tests relevant to your use case, combining input prompts that make your model fail and custom evaluation criteria
Share results, and collaborate with your team to integrate business feedback
To upload your test suite, you must have created a project on Giskard Hub and instantiated a Giskard Python client.
Then, upload your test suite like this:
test_suite.upload(giskard_client, project_key)
Here’s a demo of the Giskard Hub in action.
Troubleshooting¶
If you encounter any issues, join our Discord community and ask questions in our #support channel.

